Removing personal data from file metadata. How to access personal information. Types of hidden and personal data in Excel
The easiest way to grab the tail of a negligent employee or student who gave his report or coursework “to outsource” is to look at the author or co-authors of the document. This information is saved along with other file metadata and can later be viewed by anyone. The case takes on a particularly delicate situation if the real executor turns out to be a person familiar to the inspector: an employee of the same company or a student from the same stream. Of course, a multi-storey lie will find a way out of the situation, but no matter how it later crawled out into the light. Notice the linked users of the document in the lower right corner
A banal example, of course, but it is on it that they usually pierce.
What information can be leaked
The official Microsoft help gives what can pose a potential threat to your reputation. Here is an extract of it:
- Traces of the presence of other users, as well as indications of their edits and added comments, if you worked on the document in co-authorship.
- Discolored information in the header, footer, and watermark.
- Hidden Word text, invisible objects PowerPoint, hidden rows, columns and Excel sheets.
- Content outside of the PowerPoint slide area.
- Additional document properties and other metadata such as printer path information or email headers.
Document inspector
"Document Inspector" is a handy tool for checking files for unwanted information. It is convenient for both the sender and the recipient of the document. All you need to do is go to "Details" and run a check. A couple of clicks and five seconds will turn out all the ins and outs.

The contractor has to click on delete, and the inspector - to examine the document based on the available evidence.
Prohibition of the storage of personal data
Documents and files created by different programs invisibly carry some information in properties... It can be personal data that while they are on your computer, no one pays special attention to them. But if you decide to transfer this file to someone via Internet or using a flash drive, it is advisable to check and delete unnecessary data from file properties.
What is this personal information which may be present in file? All information in file properties can be considered personal. After all, this file was created on your computer, and you gave a name to this file or added additional information such as comments. These can be: author name, file modification date, tags, and keywords... The name of the program that created the file, date of purchase, copyright, and more.
Most often, the user passes on to others files documents and images and deleting personal data in file properties in this case it will not be superfluous.
Choose which data O file leave, and what delete you can use Windows Explorer , in file properties... To do this, on the selected file, press the right mouse button and in context menu choose "Properties". In the properties window, go to the Details tab.
Here are all the hidden extras. data and depending on the type file here you can see a pretty decent list of a wide variety of information about the document. Review the list and determine which data you would not like to pass this document on to anyone else.
By the way, information about file you can not only delete but also add directly in the properties window. But, however, not at all points. To edit the available properties, click the button opposite the item, in the "Value" section. A small edit box will appear.
If necessary deleting not editable data, at the bottom of the window properties click Remove Properties and Personal Information.
A window with an editing form will open, where you need to select the "Delete the following properties for this file" item.
Deletion of personal data
from file metadata
Files created in most popular programs have properties that are automatically filled in from the data of the computer and the program itself. Due to business reasons for files leaving the organization, this data should be deleted. For example, in MS Office documents it is necessary to remove the name of the company, the name of the author of the document and the user who last saved the document. How to do it?
The solution to the problem of removing metadata from documents can be broken down into several stages:
- Removing data from already created documents.
- Prevention of saving such data in newly created documents.
- Control of sending such data through e-mail.
For already created files, the problem is solved by the built-in tools of modern operating systems... Starting with Windows 7, it is enough to call the file properties and at the bottom of the "Details" tab select "Delete properties and personal information". By selecting several files of the same type at once, you can erase data from several documents at once.
For mass deletion of information from files, you can use special applications... For example, BatchPurifier allows you to automatically strip the metadata of 60 values from 24 file types, including office applications and graphic files (PNG, JPEG).
For new documents in the application Microsoft Office users should use the "Document Inspector" tool from the "Information" - "Find Problems" menu, which scans a document that has not yet been saved for personal data and deletes it.
In earlier Microsoft versions Office (XP or 2003), you need to install the Office 2003 / XP Add-in: Remove Hidden Data, rhd_tool extension, after which an additional Remove Hiden Data item will appear in the File menu.
In order for registration data Microsoft applications Office for newly created documents did not allow user identification, you can make the following changes in the registry:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
"Company" = "_"
"CompanyName" = "_"
"UserName" = "_"
"UserInitials" = "_"
For the changes to take effect, MS Office applications do not need to be running.
The next stage is to control the sending of hidden data via e-mail or personal information.
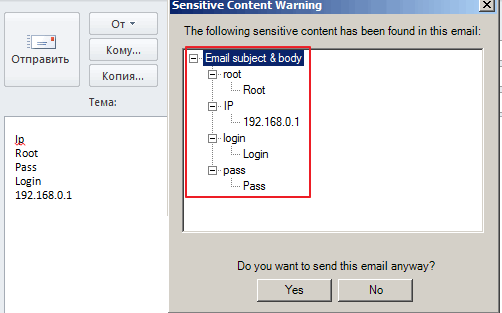
Unfortunately, there is no solution built into Microsoft Outlook. For automatic control and cleaning of documents, you can use the ConfidentSend application, which can manually or automatic mode clean up the attachment files' metadata. Also, ConfidentSend, before sending the letter, scans the message for matches with the text templates predefined by the user and, if found, issues a warning (see Fig. 2).
The Details tool allows you to view and modify important properties of a document, thereby preparing it for collaboration, archiving, or sending by e-mail... The tool provides access to several commands, which will be discussed in more detail later in the text of the book, but here we will only briefly describe their purpose.
Properties
Right side of the Details window. Each document, in addition to the content itself, carries a lot of information about who created it, what its topic is, and to which category it can be attributed. In addition, the document includes keywords describing the content of the document, notes, etc. All this information helps automated systems workflow or users to post, sort and search for the required documents. For this reason, I advise you not to be lazy and fill in the appropriate fields. The more intelligently you fill them in, the easier it will be to work with the document.
Prepare for Sharing
Document inspector- this command opens the document inspector window. Some personal information and information about your computer is inserted into the document automatically, without you noticing. For example, the name of the user under whom you created the document is contained in the document regardless of whether you filled in the property fields or not. If you printed a document or even a preview, then the full path to the local or network printer... If you inserted illustrations into the document, then the path to them is also stored in the document. If you send a document to a mailing list to a large number of different people, you may not like that such information becomes available without your knowledge. Document inspector provides search for hidden data in the document, presents it to you and allows you to delete
them from the Excel workbook.
Accessibility check- allows you to assess how convenient it will be to use these documents for users with disabilities.
Compatibility check- the team checks if it is possible this document without making changes to it open in more earlier versions Excel.
Protect book
This tool allows you to impose restrictions on the ability to change and edit the content and structure of the book.
Encrypt with a password- the document is encrypted so that you can see its contents only after entering the password. When encrypting a book with a password, be very careful about the current case of letters and keyboard layout, otherwise you risk losing access to your own book yourself.
Limit user permissions- this command is usually available only to the author of the document and users of the corporate network or the Internet. It uses a User Rights Management Server. It could be free server Microsoft or corporate server. Every time the user tries to open the document, a request is sent to the server and it returns the properties given user, in particular, information about what he can see in the opened document and what should be hidden from him. When you try to execute this command, you will be prompted to go through the registration procedure at Microsoft server... If you're interested in seeing how restrictions work, go through this procedure, register multiple users with different rights, and test this command.
Add digital signature - this command adds an invisible code to the document that replaces the usual signature. Read carefully what the signature creation wizard will write to you. If you create a personal signature, then with its help only you personally and only on this computer will be able to make sure that your document has not been changed. If you want to create a signature that will be "recognized" by external organizations, you will have to use the services of special network services.
Mark as final- after executing this command, it will be impossible to make changes to the document.
Protect current sheet- using this tool, you can specify which sheet elements can be changed by other users, and which are protected and cannot be changed.
Protect the structure of the book- prohibits changing the structure of the book (adding or removing sheets).
Versions
Lets you view and restore draft versions of unsaved files, or delete drafts that are no longer needed.
The safety of personal data should be given special attention, since since last year the legislator has toughened the liability for the employer for failure to comply with the obligation to protect them. In the article, we will tell you what is considered personal data, what obligations to protect them are established for employers and how to organize the correct accounting and storage of employees' personal data.
Systematize or update knowledge, gain practical skills and find answers to your questions on at the School of Accountants. The courses are developed taking into account the professional standard "Accountant".
An employer, when hiring an employee, must request certain information from him, which is necessary within the framework of labor, tax and accounting laws. Federal Law No. 152-FZ of 27.07.2006 "On Personal Data" requires an employer who in this case is the operator of personal data and performs their processing, to ensure the security of this information.
What data is personal
Personal data is any information directly or indirectly related to the subject of personal data - defined or determined natural person(Article 3 of the Federal Law of 27.07.2006 No. 152-FZ "On Personal Data", hereinafter - the Law on Personal Data).
General personal data includes the following information:
- Full Name;
- Date and place of birth;
- address (place of registration);
- education, profession;
- image of a person (photograph and video), which allows identification and is used for this purpose by the operator (Explanations of Roskomnadzor dated August 30, 2013 “On the issues of referring photo and video images, fingerprint data and other information to biometric personal data and the peculiarities of their processing ");
- marital status, having children, family ties;
- facts of biography and previous labor activity (place of work, criminal record, military service, work in elective positions, in public service, etc.);
- financial position. Information about wages is also personal data (letter from Roskomnadzor dated 07.02.2014 No. 08KM-3681);
- business and other personal qualities that are of an evaluative nature;
- other information that can identify a person.
In addition, the Personal Data Law mentions:
- special personal data (concerning race, nationality, political views, religious or philosophical beliefs, health status, intimate life). As a general rule, the processing of this data is not permitted. The exception is the cases provided for in part 2 of Article 10 of the Law on Personal Data;
- biometric personal data (characterize the physiological and biological characteristics of a person, on the basis of which his personality can be identified). To process such information, the consent of the subject of personal data is required. The exception is the cases established by Part 2 of Art. 11 of the Law on Personal Data.
The employer has the right to receive and use only that information that characterizes the citizen as a party to the employment contract (for example, information on the social and property status of a person is not related to his labor process). This information is contained in the following documents presented by the employee when hiring:
- in a passport or other identity document;
- work book;
- documents on military registration, education, family composition;
- certificate of income from the previous place of work;
- a questionnaire filled out for employment;
- the employee's personal card (form T-2);
- certificates of marriage, birth of a child;
- medical certificates, etc.
The employer keeps copies of the listed documents, with the exception of questionnaires, work books and personal cards.
Personal data processing
Processing of personal data - any action (operation) or a set of actions (operations) performed using automation tools or without using such tools with personal data, including collection, recording, systematization, accumulation, storage, clarification (update, change), extraction, use, transfer (distribution, provision, access), depersonalization, blocking, deletion, destruction of data (Article 3 of the Law on Personal Data).
The law on personal data obliges the employer to comply with certain requirements for the processing of this data. For example, the processing of personal data is carried out only with the consent of the employee (clause 1 of article 6, article 9 of the Law on Personal Data). In order to avoid legal disputes, it is better if this consent is made in writing. The same rule applies to job seekers.
In some cases, a written consent form is expressly provided for by law (part 4 of article 9 of the Law on Personal Data). For example, the employee's written consent to the processing of his personal data is required:
1) upon receipt of the employee's personal data from a third party (clause 3 of article 86 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). But in this case, the employee must be notified in advance of this and receive his written consent (clause 3 of article 86 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The notification must indicate (clause 3 of article 86 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- the purpose of obtaining personal data of an employee from a third party;
- prospective sources of information (persons from whom the data will be requested);
- methods of obtaining data, their nature;
- possible consequences of the employer's refusal to obtain the employee's personal data from a third party. If the employee refuses to familiarize himself with the notification of the alleged receipt of his personal data from another person, it is advisable to draw up an appropriate act.
If the employee changes his mind, then at any time he has the right to revoke his consent to the processing of personal data (part 2 of article 9 of the Law on Personal Data).
In such a situation, the continuation of the processing of the employee's personal data without his consent is possible if there are good reasons. They are listed in clauses 2 - 11 of part 1 of article 6, part 2 of article 10, part 2 of article 11 of the Law on Personal Data (part 2 of Article 9 of the Law on Personal Data).
Certain information (which is not related to the goals listed in clause 1 of Article 86 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), the employer does not have the right to request from third parties even if the employee agrees.
2) when transferring the employee's personal data to third parties, except for those cases when it is necessary to prevent a threat to the life and health of the employee (paragraph 2 of article 88 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
3) for processing special categories of employee personal data directly related to labor relations (clause 4 of article 86 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, clause 1 of part 2 of article 10 of the Law on Personal Data). This data includes information about race, nationality, political views, religious and philosophical beliefs, health status, intimate life.
If the employee is incapacitated, written consent to the processing of his data is given by his legal representative (parent, guardian) (part 6 of article 9 of the Law on Personal Data). And in the event of the death of an employee, such consent is drawn up by his heirs, unless it was received from the employee himself during his lifetime (part 7 of article 9 of the Law on Personal Data).
Not in all cases the employee's consent to the processing of personal data is required. For example, if the data is received (clause 2, part 1, article 6, clause 2.3, part 2, article 10 of the Law on Personal Data, paragraph 1 of the Roskomnadzor Clarifications):
- from the documents (information) presented when concluding an employment contract;
- based on the results of a mandatory preliminary medical examination of the state of health (Article 69 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, clause 3 of the Roskomnadzor Clarifications of December 14, 2012 "Issues concerning the processing of personal data of employees, applicants for filling vacant positions, as well as persons in the personnel reserve" , hereinafter - Explanations of Roskomnadzor dated 12/14/2012);
- in the amount provided by the unified form No. T-2, including personal data of close relatives, and in other cases established by the legislation of the Russian Federation (obtaining alimony, issuing admission to state secrets, issuing social payments) (clause 2 of the Roskomnadzor Clarifications dated 14.12. 2012);
- from a recruiting agency acting on behalf of the applicant (paragraph 12, clause 5 of the Roskomnadzor Clarifications of 12/14/2012);
- from an applicant who himself posted his resume on the Internet, making it available to an unlimited number of persons (clause 10, part 1 of article 6 of Federal Law No. 152-FZ of July 27, 2006, paragraph 12 of clause 5 of Roskomnadzor's Clarifications of 12/14/2012 ).
The employer, with the employee's consent, may entrust the processing of his personal data to another person (part 3 of article 6 of the Law on personal data, paragraph 2 of paragraph 5 of the Roskomnadzor Clarifications of 12/14/2012). But at the same time, it is the employer who is responsible to the employee for the actions of the specified person (part 5 of article 6 of the Law on Personal Data).
In Kontur.School: changes in legislation, peculiarities of accounting and tax accounting, reporting, salary and personnel, cash transactions.
Organization of accounting and storage of personal data
The employer must ensure the protection of the employee's personal data from their unlawful use or loss at their own expense (clause 7 of article 86 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
We will analyze step by step the employer's actions for recording and storing personal data in an organization.
Step 1... The employer must issue a local act that will regulate the storage and use of personal data. Such an act is usually the Regulation on the personal data of employees, with which employees must be familiarized with the signature (clause 8 of article 86 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The employee must familiarize himself with the Regulation on personal data, as well as with other local regulations, before signing an employment contract (Article 68 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). It is impossible to acquaint the employee with the document by sending it by e-mail, this will not be considered an acquaintance with the signature. In the absence of the employee's signature, the employer will not be able to prove that the employee was familiar with this document.
The Regulation on Personal Data, like any other local regulatory act, is issued and approved by an order, which is signed by the head of the organization or another person authorized for this.
In the case of an inspection of the organization, the inspection bodies can request this document and check whether the employees are familiar with it. The absence of such a document or the failure of employees to familiarize themselves with it may be grounds for bringing the employer to responsibility in accordance with Part 1 of Article 5.27 of the Administrative Offenses Code of the Russian Federation, and in the event of committing a similar violation again - under Part 2 of Article 5.27 of the Administrative Code of the Russian Federation. This conclusion is also confirmed by judicial practice (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated October 26, 2006 No. KA-A40 / 10220-06 No. A40-20745 / 06-148-194).
Step 2... The employer approves a document containing a list of personal data that are used in the activities of the organization. This document includes all the information that the employee informs about himself in writing when applying for a job, as well as used later in the preparation of personnel documentation.
In addition, the list must contain documents containing the information about employees that the organization submits to various government bodies (tax and labor inspectorates, statistics bodies).
Step 3... The employer, by order, must appoint those responsible for working with personal data and those responsible for ensuring the security of personal data. This responsibility can be either a specific person or a unit. In the latter case, the head of such a unit bears personal responsibility. This order must be brought to the attention of all employees specified in it, which must be confirmed by their signature.
Step 4... In case of verification, in order to avoid disputes with the auditors, it is better to prepare the following documents:
- employee statements of consent to the processing of personal data;
- personal data logs, their issuance and transfer to other persons and representatives of various organizations, government agencies;
- a log of checks for the availability of documents containing personal data of the employee.
Step 5... By order of the head of the organization, establish a list of storage locations for documentation that is a carrier of personal data of employees, as well as a list of measures necessary to ensure the safety of personal data, the procedure for their adoption. All documents containing personal data of employees, such as personal files, filing cabinets, accounting journals, should be stored in specially equipped cabinets or safes, which are locked and sealed. Employees' work books should be kept in a safe separately from personal files.
Let's sum up
- whether all employees gave consent to the processing of personal data;
- whether employees are familiar with local acts establishing the procedure for processing such data, and with their rights and obligations in this area;
- whether the storage and protection of personal data is properly carried out;
- whether the documentation on their processing complies with the legal requirements, etc.
